Djibouti
Djibouti
Djibouti’s population is estimated at around 1.11 million [9], with nearly 78.4 percent living in urban areas in 2022.[2] The youth population, below the age of 30, makes up 58.5 percent of the total population, and the fertility rate is at 2.76 children per woman in 2022.[9] Average life expectancy is 62.9 years, [9] lower than the regional average of 70.8 years.[3] Maternal mortality remains high at 234 deaths per 100,000 live births, compared to the regional average of 132 per 100,000 live births in 2020.[3]
Djibouti ranks among the low human development countries (171st out of 189) according to the 2021 Human Development Report.[4] Djibouti has made significant progress in its enrolment rates over the last two decades. Gross primary enrolment has more than doubled between 2000 and 2021, increasing from 32.5 percent to 73.2 percent. At the same time, gross secondary enrolment rose from 14 percent in 2000 to 55.2 percent in 2021.[3]
Because of the volatile situation in neighbouring countries, Djibouti hosts 29,577 refugees and asylum seekers, mostly originating from Ethiopia, Eritrea, Somalia, and Yemen, as of 2022.[6]
Djibouti is one of the smallest countries in the region with a total area of 23,200 square kilometers. Arable land makes up only 0.08 percent of the total land area and given Djibouti’s hot and dry climate, the agriculture, forestry, and fishing sector represents only 1.68 percent of GDP in 2020.[3] Additionally, the size of the economy limits its ability to diversify production. Hence, Djibouti largely depends on foreign markets and imports 90 percent of its food commodities, which increases the country’s vulnerability to external shocks.[7] Trade reached 223.12 percent of GDP in 2020, with trade in services being estimated at 48.23 percent of GDP in 2021. Djibouti’s economy is mainly dependent on the services sector, which represented 77.27 percent of GDP in 2020.[3]
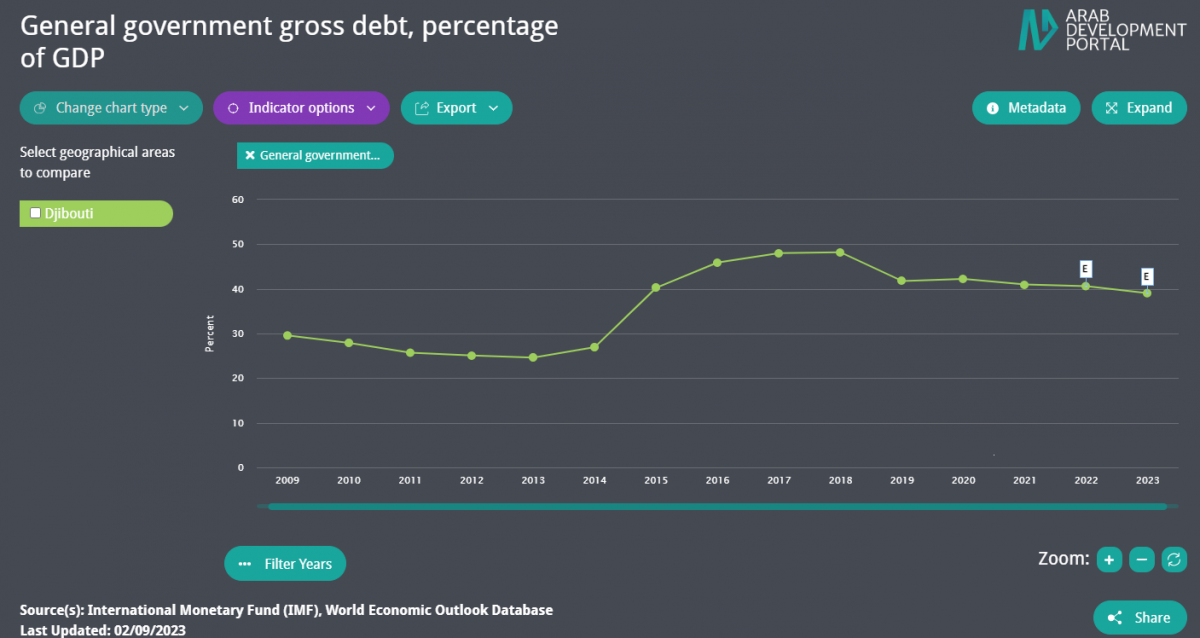
Driven by large investment projects in railway (such as the one connecting it with Addis Ababa), ports, and infrastructure, real GDP grew from 1.6 percent in 2009 to 7.2 percent in 2011, it maintained a positive growth till 2022 registering 3.18 percent and it is estimated that it will reach 5 percent in 2023.[8] Djibouti’s general government gross debt is estimated at 40.4 percent of GDP in 2022. [8]
Djibouti registered an estimated GDP (Purchasing Power Parity) of $6.607 billion in 2022.[8] The unemployment rate is higher for women in comparison to men registering 37.88 percent and 23.78 percent respectively[1]
Persistent and chronic drought and occasional flash floods are the main drivers of humanitarian needs in Djibouti. Consecutive climate shocks also have a severe impact on the lives and livelihoods. For example, in May 2018, Djibouti was hit by tropical cyclone Sagar, which affected around 10,000 households (about 150,000 people) with about 2,000 households being severely damaged, schools and other social infrastructure destroyed and access to sanitation, safe drinking water, and hygiene items among poor households further reduced.[5]
Despite its sustained growth for the last two decades, Djibouti is still affected by poverty and inequality as poverty rates stand at 79 percent, with 42 percent of the population living in extreme poverty.[7]
This overview was last updated in November 2023. Priority is given to the latest available official data published by national statistical offices and/or public institutions.
Sources:
[1] International Labor Organization. 2023. ILO stat [ONLINE] Available at: https://ilostat.ilo.org/ [Accessed 23 September 2023].
[2] Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat. 2023. World Urbanization Prospects. [ONLINE] Available at: https://population.un.org/wup/ [Accessed 23 October 2023].
[3] The World Bank. 2023. World Development Indicators. [ONLINE] Available at: https://databank.worldbank.org/data/source/world-development-indicators [Accessed 23 August 2023].
[4] United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). 2023. Human Development Index. [ONLINE] Available at: https://hdr.undp.org/data-center/documentation-and-downloads [Accessed 25 October 2023].
[5] The United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund (UNICEF). Mid-Year 2019. Djibouti humanitarian situation report. [ONLINE] Available at:
https://reliefweb.int/sites/reliefweb.int/files/resources/UNICEF%20Djibouti%20Humanitarian%20Situation%20Report%20-%20Mid%20Year%202019.pdf [Accessed 1 March 2021].
[6] United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR). 2023. Refugee Population Statistics Database. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.unhcr.org/refugee-statistics/download/ [Accessed 15 October 2023].
[7] World Food Programme (WFP). 2023. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.wfpusa.org/countries/djibouti/ [Accessed 30 November 2023].
[8] International Monetary Fund. 2023. World Economic Outlook. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/SPROLLs/world-economic-outlook-databases#sort=%40imfdate%20descending [Accessed 24 October 2023].
[9] Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat. 2023. World Population Prospects. [ONLINE] Available at: https://population.un.org/wpp/ [Accessed 23 October 2023].
Data Highlights
-
General government gross debt percent of GDP maintained a slight decrease since 2018 and reached an estimate of 39 percent in 2023.